The Vast Reach of Preventable COVID-19 Deaths: Over 20 Million Lives Touched
The Ripple Effect: Unmasking the Impact of Preventable COVID-19 Deaths
Our exploration begins with an unsettling statistic: approximately 6.17% of the U.S. population has been directly or indirectly affected by preventable COVID-19 deaths. This figure represents over 20 million people, exceeding the population of many U.S. states. The purpose of this article is to unravel the math behind this number and explore the personal and communal effects of these deaths.
Source of Data: The data comes from a study released in May 2022 by the Brown School of Public Health and Microsoft AI for Health. The study estimated that there were around 319,000 preventable adult COVID-19 deaths, given an ideal scenario where all eligible individuals were vaccinated.
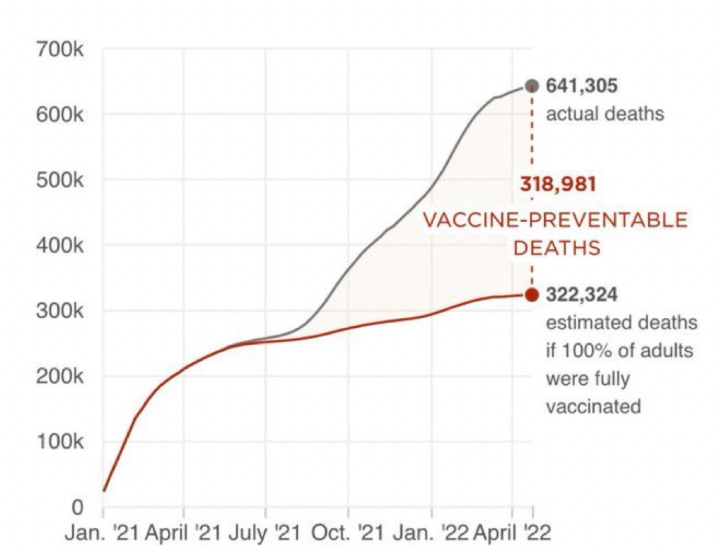
The Direct Impact: To understand the magnitude of the impact, we start with the direct connections of the deceased. Assuming each of the 319,000 deceased individuals had around ten immediate relations, the direct impact touches 3.19 million people.
The Indirect Impact: Going beyond immediate relations, we consider the broader societal impacts. We break down the indirect impact into three groups: coworkers, community contacts, and healthcare workers.
- Coworkers: With an average of 19 coworkers per deceased, the total extends by an additional 6.06 million people.
- Community contacts: Considering about 30 contacts per deceased, we’re looking at another 9.57 million people affected.
- Healthcare workers: Each deceased patient impacts an average of 5 healthcare workers, accounting for an extra 1.6 million people.
Cumulatively, these indirect impacts affect approximately 17.23 million people.
The Cumulative Impact: Adding the direct and indirect impacts together gives us a shocking total of 20.42 million people impacted by preventable COVID-19 deaths. This figure translates to approximately 6.17% of the U.S. population, based on the 2021 population of 331 million.
Political Factors: However, the impact isn’t uniform across the board. Data shows significant differences in vaccination rates along political lines, leading to higher COVID-19 mortality rates in some groups, according to the New Yorker.
For instance, research indicates that areas controlled by a Republican trifecta of governor, Senate, and House experienced an 11% higher death rate. The excess death rate among Republicans compared to Democrats rose dramatically after vaccines became available, indicating a strong correlation between political affiliation and vaccine hesitancy.
Conclusion: While these figures are built on averages and typical interactions, they underscore the far-reaching consequences of personal choices.
Each decision not to vaccinate doesn’t just risk one life, but sends ripples through families, workplaces, communities, and the healthcare system. The choice to vaccinate or not isn’t just a personal decision, but a decision that profoundly affects us all. This realization underscores the importance of understanding the science behind vaccines and encourages unity in our approach to tackling this public health crisis.

